Gabapentin (Neurontin) is a medication commonly prescribed for nerve pain, seizures, and anxiety. Although it is not considered highly addictive, stopping gabapentin suddenly after long-term use can lead to withdrawal symptoms. Many people wonder:
How long do gabapentin withdrawal symptoms last?
What are the most common withdrawal symptoms?
How can you reduce discomfort during withdrawal?
In this guide, we’ll break down the gabapentin withdrawal timeline, symptoms, and strategies for a smooth recovery.
What Causes Gabapentin Withdrawal?
Gabapentin affects the brain’s GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) system, which helps regulate nerve activity. Over time, the brain adapts to the presence of gabapentin. If the drug is stopped suddenly, the nervous system may become overactive, which can cause withdrawal symptoms.
Who Is at Risk for Gabapentin Withdrawal?
People taking high doses (900 mg/day or more)
Those using gabapentin for long periods (months to years)
Individuals with a history of substance dependence
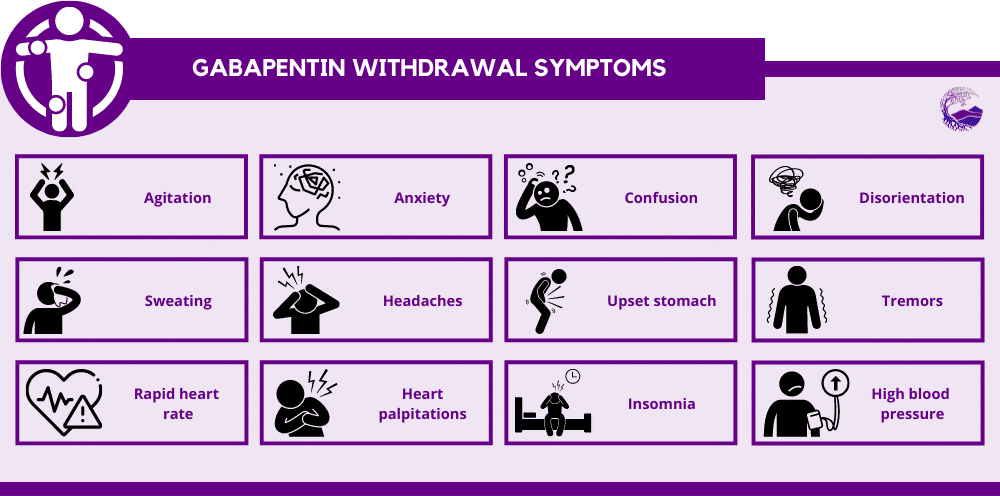
Common Gabapentin Withdrawal Symptoms
Withdrawal symptoms vary in intensity but may include:
Physical Symptoms:
- Insomnia or sleep disturbances
- Headaches
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sweating and fever-like symptoms
- Muscle pain and tremors
Psychological Symptoms
- Anxiety and panic attacks
- Depression or mood swings
- Irritability and agitation
- Confusion or brain fog
Severe (But Rare) Symptoms:
- Seizures (more likely in those with epilepsy)
- Suicidal thoughts (requires immediate medical help)
How Long Do Symptoms Last?
The duration of withdrawal depends on:
- Dosage and duration of use
- Individual metabolism
- Whether tapering was done properly
General Gabapentin Withdrawal Timeline
| Phase | Timeline | Symptoms |
| Early Withdrawal | 24–48 hours after last dose | Anxiety, insomnia, headaches |
| Peak Withdrawal | Days 3–7 | Increased anxiety, nausea, sweating |
| Subacute Phase | Weeks 1–2 | Mood swings, fatigue, lingering insomnia |
| Post-Acute (PAWS) | Weeks to months (rare) | Mild anxiety, occasional cravings |
How to Safely Manage Gabapentin Withdrawal
1. Taper Off Gradually (Under Medical Supervision)
- Fast taper (1–2 weeks): For short-term users.
- Slow taper (4–8 weeks): For long-term/high-dose users.
Example Taper Plan:
- Week 1: Reduce dose by 25%
- Week 2–4: Decrease by 10–15% weekly
2. Stay Hydrated & Eat Nutritious Foods
- Dehydration worsens symptoms.
- Magnesium and B vitamins may help with nerve function.
3. Manage Symptoms Naturally
- For anxiety: Meditation, deep breathing, or prescribed anti-anxiety meds (if needed).
- For insomnia: Melatonin or sleep hygiene practices.
- For pain: Gentle exercise, warm baths, or OTC pain relievers (consult a doctor first).
4. Seek Professional Help If Needed
- If symptoms are severe (seizures, suicidal thoughts), seek emergency care.
- A doctor may prescribe short-term medications (like clonidine) to ease withdrawal.
Can You Prevent Gabapentin Withdrawal?
Yes! The best way to avoid withdrawal is to:
✔ Follow a doctor’s tapering plan (never quit cold turkey).
✔ Monitor symptoms and adjust the taper if needed.
✔ Use gabapentin only as prescribed (avoid recreational use).
How Long Does Gabapentin Stay in Your System?
Half-life: 5–7 hours (takes about 1–2 days to leave the bloodstream).
Detection in urine: Up to 3 days (longer for heavy users).
This short half-life is why withdrawal can start within a day of stopping.
When to See a Doctor
Contact a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Seizures
- Severe depression or suicidal thoughts
- Hallucinations or extreme confusion
- Uncontrollable vomiting or dehydration
Final Thoughts
Gabapentin withdrawal typically lasts 1–2 weeks, but some may experience lingering effects. The best way to minimize discomfort is by tapering slowly under medical guidance.
If you’re planning to stop gabapentin, work with your doctor to create a safe withdrawal plan. Recovery is possible, and the right approach can make the process much smoother.
FAQs About Gabapentin Withdrawal
1. Can gabapentin withdrawal be life-threatening?
Rarely, but seizures can occur in high-dose users. Medical supervision is crucial.
2. Does gabapentin withdrawal cause depression?
Yes, mood changes are common but usually temporary.
3. How can I sleep during gabapentin withdrawal?
Try melatonin, valerian root, or prescription sleep aids (if needed).
4. Can exercise help with withdrawal symptoms?
Yes, light exercise (walking, yoga) can reduce anxiety and improve mood.
5. Is gabapentin withdrawal similar to benzo withdrawal?
Less severe, but some symptoms (anxiety, insomnia) overlap.
Conclusion
Gabapentin withdrawal is manageable with the right approach. By tapering slowly, staying hydrated, and seeking support, most people recover within 1–2 weeks.
If you or someone you know is struggling with gabapentin withdrawal, consult a doctor for a personalized plan. You don’t have to go through it alone!
Have you experienced gabapentin withdrawal? Share your tips in the comments below!



