Gabapentin for Alcohol Withdrawal can be a difficult and sometimes dangerous process for those trying to quit drinking. Symptoms like anxiety, tremors, seizures, and insomnia can make recovery difficult. Fortunately, medications like gabapentin have shown promise in reducing withdrawal symptoms and supporting long-term sobriety.
- Recommended dosage and administration
- Potential side effects and risks
- Alternatives to gabapentin
By the end, you will have a clear idea of whether gabapentin can be helpful in your or a loved one’s journey to recovery.
Table of Contents
What Is Gabapentin?
Gabapentin (brand names Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medication primarily used to treat:
- Neuropathic pain (nerve pain)
- Epilepsy and seizures
- Restless legs syndrome (RLS)
Recently, it has gained attention for its off-label use in alcohol withdrawal and dependence. Unlike benzodiazepines (traditional withdrawal treatments), gabapentin is non-addictive and carries a low risk of abuse.
How Does Gabapentin Work for Alcohol Withdrawal?
Gabapentin affects the GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) system in the brain, which is also affected by alcohol. Chronic alcohol use disrupts the function of GABA, which can lead to withdrawal symptoms when you stop drinking. Gabapentin helps:
- Calming overactive nerve signals (reducing anxiety and seizures)
- Stabilizing mood (helping with irritability and depression)
- Improving sleep (alleviating insomnia common in withdrawal)
Is Gabapentin Effective for Alcohol Withdrawal?
Several studies suggest gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal can be beneficial:
Reduces withdrawal symptoms:
A 2015 study in JAMA Internal Medicine found gabapentin significantly reduced insomnia, cravings, and anxiety in alcohol-dependent patients.
Helps maintain sobriety:
Research indicates gabapentin may lower relapse rates by decreasing the desire to drink.
Safer than benzodiazepines:
Unlike benzos, gabapentin has a lower risk of dependence and overdose.
However, it may not be suitable for severe withdrawal cases (like delirium tremens), where benzodiazepines are still the gold standard.
Gabapentin Dosage for Alcohol Withdrawal
There’s no one-size-fits-all dosage, but common guidelines include:
For Mild to Moderate Withdrawal
Day 1-3: 300–600 mg, 3 times daily (900–1800 mg total)
Day 4-7: Gradually taper down to 600–1200 mg/day
Maintenance (if needed): 300–600 mg/day to prevent relapse
For Severe Withdrawal (Under Medical Supervision)
Higher doses (up to 2400 mg/day) may be used in hospital settings.
Common side effects of gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal:
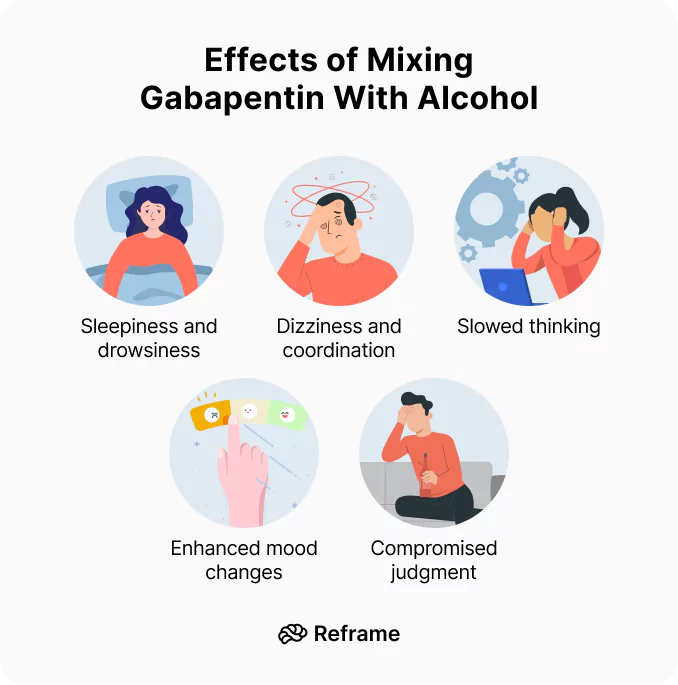
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Nausea
- Less common but serious side effects:
- Mood changes (suicidal thoughts in rare cases)
- Swelling in extremities
- Severe rash
Who Should Avoid Gabapentin?
People with kidney disease (dosage adjustments needed)
Those allergic to gabapentin or pregabalin
Pregnant or breastfeeding women (consult a doctor first)
Final Thoughts: Is Gabapentin Right for You?
Gabapentin offers a safer, non-addictive option for managing alcohol withdrawal symptoms, especially for those with mild to moderate dependence. However, it’s not a standalone cure; medical supervision, therapy, and support groups (like AA) are crucial for long-term recovery. If you or someone you know is struggling with alcohol withdrawal, consult a healthcare provider to determine if gabapentin is a suitable treatment option.
FAQs About Gabapentin for Alcohol Withdrawal
1. Can I take gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal at home?
Mild cases may be managed at home with a doctor’s guidance, but severe withdrawal requires medical supervision.
2. How quickly does gabapentin work for withdrawal symptoms?
Effects can be felt within a few hours, with peak benefits in 1–2 days.
3. Can gabapentin be used long-term for alcohol cravings?
Yes, some studies support its use for relapse prevention, but long-term use should be monitored.
4. Is gabapentin addictive?
It has a low addiction risk compared to benzos, but misuse is possible.
5. Can I drink alcohol while taking gabapentin?
No alcohol can worsen side effects and reduce the medication’s effectiveness.
Conclusion
Gabapentin is a promising tool for alleviating alcohol withdrawal symptoms and supporting recovery. While not a magic pill, it can make the detox process safer and more manageable when combined with professional care.
If you’re considering gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal, speak with a healthcare provider to create a personalized treatment plan. Recovery is possible, and the right support can make all the difference.



